- Our Services
- CDM Regulations & Principal Designer
CDM Regulations & Principal Designer
T: 0161 518 8671
E: bc@roger-hannah.co.uk
The CDM Regulations apply to all building and construction works which include New Build projects, demolition, refurbishment, extensions, conversions, repair and maintenance works.
Under the Regulations, a client must appoint a Principal Designer to plan, manage and monitor the pre-construction phase and co-ordinate matters relating to Health & Safety during the pre-constructions phase. This ensures projects are carried out without risk.
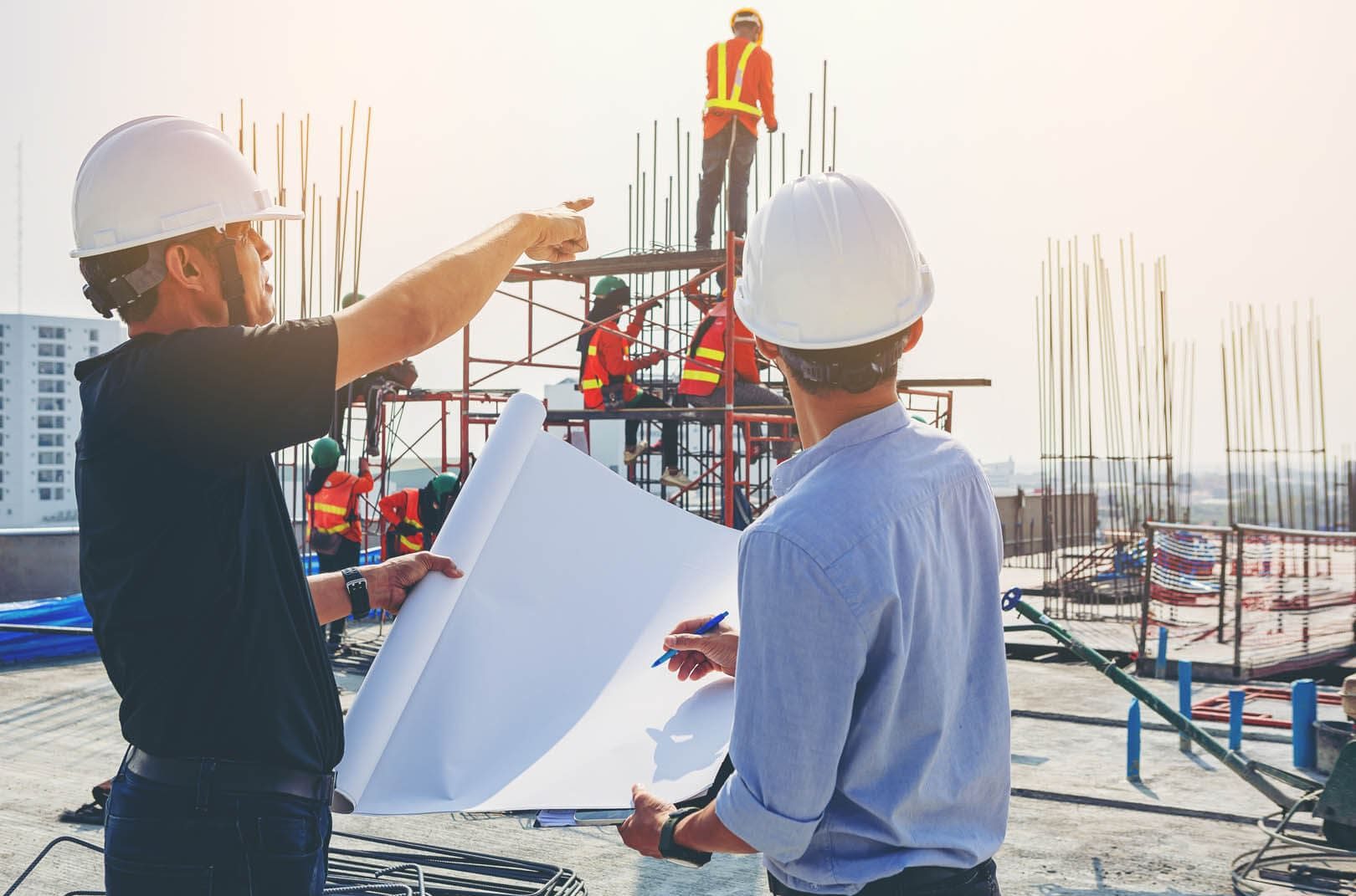

Roger Hannah can assemble an appropriate design team with the necessary experience that will satisfy the requirements of the CDM legislation, with an appointed Principal Designer.
Key contacts
Related Services
Academies & Colleges
At Roger Hannah we understand the pressures that schools face in ensuring their buildings are maintained and up to standard…
Find out more
Commercial Building Surveys
Property Acquisition is one of the most significant costs for many companies and investors; and commercial building surveys are important…
Find out more
Dilapidations
Whether you are a commercial property landlord, tenant, owner or occupier and need dilapidations advice, our team can help you…
Find out more
Insurance Surveying Services
We provide independent surveying expertise for private clients, major loss adjusters and insurers with nationwide capability. Our surveyors work across…
Find out more
Party Wall Services
Are you or your neighbour building close to an adjoining wall? Our experienced Party Wall Act Surveyors act on behalf…
Find out more